March 4, 2015
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, Baby Woolly Rhino, business, Business News, Daily Discovery, Fossils, Hotels, Huffpost Science Click, human-rights, medicine, mental-health, Paleontology, permafrost, Prehistoric Rhino, Prehistoric Woolly Rhino, Prehistory, research, Rhino Sasha, Sakha Republic, Science, Science News, Siberia, technology, Technology News, travel, vacation, Video, Woolly Rhino, Woolly Rhino Sasha, Woolly Rhino Siberia
FROM
Huffpost Science
Click link below picture
.
Scientists are going gaga over the recent discovery of a baby woolly rhino.
The pristine specimen of the tiny extinct rhino–the only one of its type ever found–was discovered in permafrost along the bank of a stream in Siberia’s Sakha Republic, The Siberian Times reported.
“At first we thought it was a reindeer’s carcass, but after it thawed and fell down we saw a horn on its upper jaw and realized it must be a rhino,” Alexander ‘Sasha’ Banderov, the hunter who made the discovery, told the Times. “The part of the carcass that stuck out of the ice was eaten by wild animals, but the rest of it was inside the permafrost and preserved well.”
.
 (Academy of Sciences Republic of Sakha/Siberian Times)
(Academy of Sciences Republic of Sakha/Siberian Times)
.
.
Click link below for story, video and slideshow:
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2015/02/25/woolly-rhino-baby-siberia-photos_n_6752892.html?cps=gravity_2450_8475506239920379933
.
__________________________________________
November 7, 2014
Mohenjo
Science
Adocus Turtle, amazon, Ancient Turtle, business, Business News, Daily Discovery, Fossils, gray rocks, Hotels, huffingtonpost, human-rights, Jeff Dornbusch, medicine, mental-health, Microscopic Images, New Mexico, New Mexico Museum of Natural History, Prehistoric Turtle, Prehistory, research, Science, Science News, Slideshow, southern New Mexico desert, technology, Technology News, Tom Suazo, travel, Truth or Consequences, Turtle Fossil, Turtle Fossil New Mexico, vacation
Click link below picture
.
Jeff Dornbusch knew there was something odd about a pile of gray rocks he spotted more than a decade ago during a hike in the southern New Mexico desert, and a closer look confirms that he was right.
Dornbusch, a museum volunteer in Truth or Consequences, N.M., relocated those rocks in 2012 and notified local scientists, who identified the rocks as fragments of a 90-million-year-old turtle fossil, the Las Cruces Sun-News reported.
Since then, researchers have returned to the site where the rocks were found and excavated the rest of the turtle.
.
 Workers from the New Mexico Museum of Natural History (from left, Tom Suazo, fossil preparer; Amanda Cantrell, geosciences collections manager; Jake Sayler, volunteer; and Asher Lichtig, student researcher) excavating the 90-million-year-old turtle fossil on Oct. 29, 2014, about six miles east of Turtleback Mountain, a well-known peak near Truth or Consequences.
Workers from the New Mexico Museum of Natural History (from left, Tom Suazo, fossil preparer; Amanda Cantrell, geosciences collections manager; Jake Sayler, volunteer; and Asher Lichtig, student researcher) excavating the 90-million-year-old turtle fossil on Oct. 29, 2014, about six miles east of Turtleback Mountain, a well-known peak near Truth or Consequences..
.
Click link below for story and slideshow:
.
__________________________________________
December 4, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, anthropology, Archaeology, business, Business News, Hotels, huffingtonpost, human-rights, May Help Reveal How Stones Were Moved, medicine, mental-health, mystery of Stonehenge, NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC, Prehistory, research, Science, Science News, Slideshow, Stonehenge, Stonehenge Mystery, Stonehenge Rock, Stonehenge Rock Origin, Stonehenge Rock Origins Pinpointed In Wales, Stonehenge Rocks, Stonehenge Rocks Origin, stones, technology, Technology News, travel, Unearthed, vacation, Video
FROM

Click link below picture
.
Are we one outcrop closer to unraveling the mystery of Stonehenge?
For years researchers have tried to pinpoint exactly where the enormous stones used in the English monument came from–and how they ended up on an otherwise grassy Salisbury Plain.
It’s long been thought that the iconic monument’s outer stones were hauled from a sandstone quarry situated 20 to 30 miles away, National Geographic reported. The inner stones, however, have presented a tougher question.
Currently, there are two prevailing theories about the inner stones’ origins. One is that an ancient glacier simply pushed them near to the site where the monument was erected, according to NatGeo. The other is that they were somehow hauled there by some exceedingly enterprising early humans.
Now a team of researchers say they’ve located the rocky Welsh hill where some of Stonehenge’s inner stones originated. The team — made up of archaeologists and geologists from several United Kingdom institutions — claim to have matched a type of stone found at Stonehenge, called a spotted dolerite bluestone, to the Carn Goedog outcrop in Wales, the BBC reported.
.
.
.
Click link below for story, video and slideshow:
.
__________________________________________
November 28, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, Ancient Human Breeding, ancient human history, Ancient Human Interbreeding, Ancient Human Sex, Ancient Humans, Ancient Humans Sex, anthropology, business, Business News, Denisovans, Denisovans Humans, evolution, Hotels, huffingtonpost, human-rights, Humans Neanderthals, Humans Neanderthals Breeding, LONDON, Mark Thomas, medicine, mental-health, Modern Humans, neanderthals, Prehistory, research, Royal Society, Science, Science News, Slideshow, technology, Technology News, travel, University College London, vacation, Video
FROM

Click link below picture
.
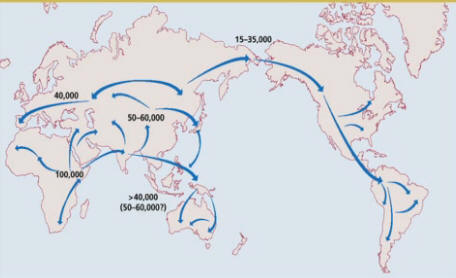
The ancient genomes, one from a Neanderthal and one from a different archaic human group, the Denisovans, were presented on 18 November at a meeting at the Royal Society in London. They suggest that interbreeding went on between the members of several ancient human-like groups living in Europe and Asia more than 30,000 years ago, including an as-yet unknown human ancestor from Asia.
“What it begins to suggest is that we’re looking at a ‘Lord of the Rings’-type world — that there were many hominid populations,” says Mark Thomas, an evolutionary geneticist at University College London who was at the meeting but was not involved in the work.
The first Neanderthal and the Denisovan genome sequences revolutionized the study of ancient human history, not least because they showed that these groups interbred with anatomically modern humans, contributing to the genetic diversity of many people alive today.
.
.
.
Click link below for story, video and slideshow:
.
__________________________________________
October 24, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, Ancient Human Skull, anthropology, Archaeology, biology, business, Business News, Daily Discovery, evolution, Health, Homo erectus, Homo ergaster, Homo habilis, Homo sapiens, Hotels, huffingtonpost, Human Ancestors, Human Evolution, human family tree, Human Skull Georgia, human species, human-rights, mental-health, Paleontology, Prehistoric Skull, Prehistory, research, Science, Science News, Skull 5, Skull 5 Humans, Slideshow, Smarter Ideas, technology, Technology News, travel, vacation, Video
FROM

Click link below picture
.
The earliest, now-extinct human lineages, once thought to be multiple species, may actually have been one species, researchers now controversially suggest.
Modern humans, Homo sapiens, are the only living member of the human lineage, Homo, which is thought to have arisen in Africa about 2 million years ago at the beginning of the ice age, also referred to as the Pleistocene Epoch. Many extinct human species were thought to once roam the Earth, such as Homo habilis, suspected to be among the first stone-tool makers; the relatively larger-brained Homo rudolfensis; the relatively slender Homo ergaster; and Homo erectus, the first to regularly keep tools it made.
To learn more about the roots of the human family tree, scientists investigated a completely intact, approximately 1.8-million-year-old skull excavated from the medieval hilltop town of Dmanisi in the Republic of Georgia. Archaeological excavations there about 30 years ago unexpectedly revealed that Dmanisi is one of the oldest-known sites for ancient human species out of Africa and the most complete collection of Homo erectus skulls and jaws found so far. The world’s largest, extinct cheetah species once lived in the area, and scientists cannot rule out whether it fed on these early humans.
.
 An artist’s conception revealing what “Skull 5” may have looked like some 1.8 million years ago when he (the scientists suspect the remains come from a male) lived.
An artist’s conception revealing what “Skull 5” may have looked like some 1.8 million years ago when he (the scientists suspect the remains come from a male) lived..
.
Click link below for story, video and slideshow:
.
______________________________________________________________________________
October 18, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, anthropology, Archaeology, Balls Mesopotamia, business, Business News, Christopher Woods, clay balls, Clay Balls Mesopotamia, Hotels, huffingtonpost, human-rights, mental-health, Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia Clay Balls, Mesopotamia Code, Mesopotamian Code, Oriental Institute, Prehistoric Code, Prehistory, research, Science, Science News, Secret Code Mesopotamia, Slideshow, technology, Technology News, travel, Unearthed, vacation
FROM

Click link below picture
.
Researchers studying clay balls from Mesopotamia have discovered clues to a lost code that was used for record-keeping about 200 years before writing was invented.
The clay balls may represent the world’s “very first data storage system,” at least the first that scientists know of, said Christopher Woods, a professor at the University of Chicago’s Oriental Institute, in a lecture at Toronto’s Royal Ontario Museum, where he presented initial findings.
The balls, often called “envelopes” by researchers, were sealed and contain tokens in a variety of geometric shapes — the balls varying from golf ball-size to baseball-size. Only about 150 intact examples survive worldwide today.
The researchers used high-resolution CT scans and 3D modeling to look inside more than 20 examples that were excavated at the site of Choga Mish, in western Iran, in the late 1960s. They were created about 5,500 years ago at a time when early cities were flourishing in Mesopotamia.
.

Anna Ressman/Courtesy Oriental Institute of the Un
Archaeologists are using CT scanning and 3D modelling to crack a lost prehistoric code hidden inside clay balls, dating to some 5,500 years ago, found in Mesopotamia.
.
.
Click link below for story and slideshow:
.
______________________________________________________________________________
August 28, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
amazon, Ancient Proteins, biology, business, Business News, chemistry, climate, deep sea hydrothermal vents, early earth, Earth, evolution, Fossil Proteins, Fossils, Hotels, html ref, Paleontology, physical chemist, Prehistory, Protein Fossils, research, Science, Science News, Slideshow, Space, Space Rocks, technology, Technology News, travel, university of granada, vacation
FROM

Click link below picture
.
Researchers have reconstructed the structure of 4-billion-year-old proteins.
The primeval proteins, described today (Aug. 8) in the journal Structure, could reveal new insights about the origin of life, said study co-author José Manuel Sanchez Ruíz, a physical chemist at the University of Granada in Spain.
Exactly how life emerged on Earth more than 3 billion years ago is a mystery. Some scientists believe that lightning struck the primordial soup in ammonia-rich oceans, producing the complex molecules that formed the precursors to life. Others believe that chemical reactions at deep-sea hydrothermal vents gave rise to cell membranes and simple cellular pumps. And still others believe that space rocks brought the raw ingredients for life — or perhaps even life itself — to Earth.
But it’s difficult to recreate events that happened so far in the distant past.
.

The individual molecules within early Earth’s primordial soup that form the basis of life likely developed in response to natural selection.
.
.
Click link below for story and slideshow:
.
______________________________________________________________________________
March 17, 2013
Mohenjo
Science
aviation, biology, climate, De-Extinction, Dna, Extinct Animals, gaming, Gastric Brooding Frogs, nature, Polls, Prehistory, Science, Science News, Tedxdeextinction, transportation, Video, Woolly Mammoth, Wooly Mammoth, Wooly Mammoth Clone, Zoology
FROM

Click link below picture
.
Biologists briefly brought the extinct Pyrenean ibex back to life in 2003 by creating a clone from a frozen tissue sample harvested before the goat’s entire population vanished in 2000. The clone survived just seven minutes after birth, but it gave scientists hope that “de-extinction,” once a pipedream, could become a reality.
Ten years later, a group of researchers and conservationists gathered in Washington, D.C., today (March 15) for a forum called TEDxDeExtinction, hosted by the National Geographic Society, to talk about how to revive extinct animals, from the Tasmanian tiger and the saber-toothed tiger to the woolly mammoth and the North American passenger pigeon.
.

This photo shows a museum worker inspecting a replica of a woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius), a relative of modern elephants that went extinct 3,000 to 10,000 years ago.
.
.Click link below for story, slideshow, and video:
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/03/15/de-extinction-wooly-mammoth-poll_n_2888386.html?utm_hp_ref=science
.
____________________________________________________
 (Academy of Sciences Republic of Sakha/Siberian Times)
(Academy of Sciences Republic of Sakha/Siberian Times) Workers from the New Mexico Museum of Natural History (from left, Tom Suazo, fossil preparer; Amanda Cantrell, geosciences collections manager; Jake Sayler, volunteer; and Asher Lichtig, student researcher) excavating the 90-million-year-old turtle fossil on Oct. 29, 2014, about six miles east of Turtleback Mountain, a well-known peak near Truth or Consequences.
Workers from the New Mexico Museum of Natural History (from left, Tom Suazo, fossil preparer; Amanda Cantrell, geosciences collections manager; Jake Sayler, volunteer; and Asher Lichtig, student researcher) excavating the 90-million-year-old turtle fossil on Oct. 29, 2014, about six miles east of Turtleback Mountain, a well-known peak near Truth or Consequences.